Gum disease most commonly affects adults.
Gum disease is a broad term that refers to different stages of gum inflammation and infection caused by poor oral hygiene. Left untreated, it can lead to serious complications like tooth loss. That being said, gum disease is easily preventable and can be reversed when detected early.
If you suspect that you have gum disease because of red, swollen or bleeding gums, or just want to know more about how you can prevent it, then this article is for you. Here, we break down what gum disease is, as well as explain its causes, symptoms, treatments and costs.
This article will cover the following topics:
What is gum disease?
You may have come across the terms ‘gingivitis’ and ‘periodontitis’ – the two main stages of gum disease.
Gingivitis is an earlier stage and milder form of gum disease. It is a gum inflammation that occurs when plaque, a naturally occurring biofilm containing bacteria, accumulates on the soft tissues around your teeth, causing the gums to bleed or appear red and puffy.
If it is not treated, gingivitis can develop into periodontitis, a gum infection that damages the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth. Often, the damage caused at this stage is irreversible. While gingivitis is often a precursor to periodontitis, it does not always lead to periodontitis. If detected early and treated, it can be reversed by professional cleaning and good oral hygiene.
What causes gum disease?
Without proper brushing and flossing, dental plaque (a thin, sticky film of bacteria, protein and debris) starts to form on your teeth. Over time, the plaque that builds up hardens to form tartar at the gum line. Unlike dental plaque, which can be gently cleaned off with the help of good oral hygiene habits, tartar is more stubborn to remove and requires professional cleaning by a dentist or dental hygienist to remove. If the tartar is not removed, it may irritate the gum tissue around the base of your teeth. This leads to gingivitis, and if not treated, periodontitis.
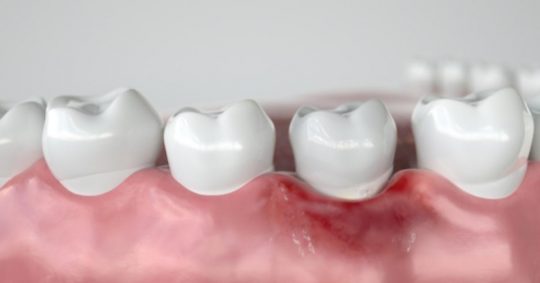
Those suffering from periodontitis may experience receding gums.
When tartar builds up over time, the gum tissues start to recede and deep gum pockets that collect plaque and bacteria start to develop. This leads to progressive gum and bone loss, damaging the structures that hold your teeth in place. If not treated, this might cause teeth to become loose, feel painful, or even come out completely.
What are the complications of gum disease?
Without treatment, gingivitis can develop into periodontitis – where the infection reaches the soft tissue and bone. If periodontitis is left untreated, there can be serious complications such as loss of teeth and acute infections.
Besides tooth loss, gum disease is a risk factor for a range of other health problems, such as diabetes[1], coronary heart disease[2] and stroke[3]
What are the symptoms of gum disease?
Bleeding gums while brushing is a common symptom of gum disease.
During its early stages, gum disease may go unnoticed as it does not always cause symptoms like pain or discomfort. However, some initial symptoms include red, tender and swollen gums, as well as bad breath. Your gums may bleed easily during brushing or flossing, and you might also find chewing painful.
In more advanced stages of periodontal disease, you might notice some of these symptoms:
- Receding gums
- Teeth shifting from position
- Gaps between teeth become wider
- Change in bite
- Tooth sensitivity
How do dentists diagnose gum disease?
Firstly, the dentist will examine your gums for any signs of inflammation. They may also want to find out more about your medical history and habits to see if there is anything that may put you at a greater risk of gum disease (more on these risk factors later).
Additionally, your dentist may measure the depth of your gum pockets. You may also be asked to take an X-ray to get a better look at the remaining bone support around the tooth.
How is gum disease treated?
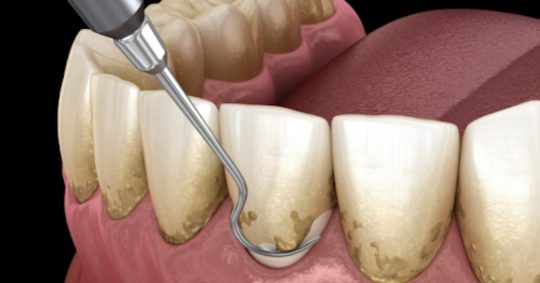
A dental scaler is used during root planing to remove hardened plaque.
There is a wide range of gum treatment options available, though their suitability depends on the person’s needs. In this section, we look at some of the more common procedures to treat gum disease, including those we offer here at NTUC Health Denticare.
Non-surgical treatments
- Scaling: Scaling is a routine procedure done during your twice yearly visits to the dentist. It helps to remove plaque buildup and stubborn tartar. Using professional dental instruments, the dentist will clean away the plaque and tartar from below the gum line. Depending on your condition, multiple sessions may be required in order to thoroughly clean your teeth.
- Root planing: Root planing, usually done right after scaling, is a deep-cleaning procedure done under local anaesthesia to gain access to plaque and tartar which resides deeper under the gum line. The dentist will smooth out rough spots on the root surfaces. This helps to remove bacteria and provide a smooth, clean surface for the gums to reattach to the tooth.
- Antibiotic treatment: The dentist may prescribe you with antibiotics to minimise bacterial infection. This can be in the form of oral or topical antibiotics.
Surgical treatments
- Periodontal surgery: Periodontal surgery (sometimes known as flap surgery) is usually recommended when there is a significant separation between the gum and teeth. During the procedure, the gums are first lifted back to reveal the extent of the hardened tartar which is later removed. In some cases, the damaged bone around the infected teeth is smoothed out to quicken the healing process and minimise potential areas where bacteria can grow.
- Regenerative procedures: Gum and bone grafting are two common regenerative procedures. Gum grafting helps to repair damaged gums that are thin or have receded. Often, the grafted gum tissue is taken from the roof of the mouth and stitched in place at the affected area. On the other hand, bone grafting is used to enhance areas with deficient bone to facilitate bone regrowth and dental implant placement.
- Guided tissue regeneration*: Guided tissue regeneration is a less common procedure that is performed when the bone supporting the teeth is destroyed. A mesh-like fabric is inserted between the bone and gum tissue, to allow the bone and connective tissue to regrow and better support the teeth.
*NTUC Health Denticare does not provide guided tissue regeneration services at this moment.
How much does gum disease treatment cost?
At NTUC Health Denticare, we offer affordable gum treatment options. Check out the fees in the table below:
| Scaling & Polishing | $70.00 onwards |
| Root Planing | $170.00 onwards |
| Periodontal Surgery | $280.00 – $400.00 |
| Regenerative Procedures | From $890.50 |
CHAS subsidies are available for scaling and polishing, up to twice per calendar year:
| Dental Service | CHAS Orange | CHAS Blue | Merdeka Generation | Pioneer Generation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scaling | – | $50.50 | $60.50 | $70.50 |
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Why should I visit the dentist twice a year?
We recommend that you visit your dentist at least once every 6 months for a routine check-up and professional dental cleaning. Regular dental visits make sure that any problems can be detected and treated early.
Additionally, thorough cleaning by a dental professional can prevent or reverse gum disease by removing built-up plaque and tartar. In the long run, it can also help you save money, since complications caused by gum disease are more expensive and difficult to treat.
-
What can I do to prevent gum disease?
The most effective thing you can do to prevent gum disease is to maintain good oral hygiene, even if you have just undergone gum treatment.
You can improve your oral health by brushing your teeth twice daily and flossing them at least once a day. Thorough brushing and flossing helps to remove plaque before it starts to build up. You can also consider using a fluoride toothpaste and visiting the dentist twice yearly for professional cleaning and check-ups.
Additionally, there are some things that can put you at a greater risk of gum disease, one of the most significant risk factors being smoking. Giving up smoking can go a long way in improving your oral hygiene. Another risk factor is misaligned or crowded teeth since it is easier for food particles to get trapped. Correcting them through orthodontic treatment and braces can help improve your oral health and minimise your risk of gum disease.
-
Will I be able to resume daily activities after treatment?
With scaling and polishing, you will be able to return to regular activities immediately. For root planing, sensitivity and soreness following the procedure is normal, but should not interfere with your daily activities. However, for more invasive procedures, such as flap surgery, you may require more rest.
-
How long will the procedure take?
This depends on the type of gum treatment and the severity of your gum condition. Simpler procedures take about 30 minutes, while more complex ones can take up to 2 hours. If your condition is more severe, your dentist may recommend spreading the procedures over several weeks to help with wound healing.
-
When should I see a periodontist (a.k.a. gum specialist)?
Periodontal disease may not cause any obvious symptoms, such as pain or discomfort, in its early stages. Therefore, it is important that you visit the periodontist regularly as well. Those in their twenties should be examined by a periodontist at least once every 4 years, while those above the age of 30 should have theirs checked every 3 years.
-
Can gum disease be reversed?
Gum disease is reversible only in its early stages (i.e. gingivitis). This can be accomplished with the help of non-surgical gum treatment options, such as scaling and root planing, together with good oral hygiene. However, if not treated, gum disease can cause irreversible damage to the gums and bone, which would then require more invasive and extensive treatment.
-
Is gum disease contagious?
Gum disease is not contagious. However, bacteria that cause gingivitis can spread through saliva. This increases the other person’s risk of getting gingivitis, especially if they have poor oral hygiene too.
Summary
Good oral hygiene and regular dental visits are essential to having healthy gums and teeth. Each trip to the dentist is a chance for you to get your teeth professionally cleaned, as well as for the dentist to examine your teeth and gums.
When it comes to gum disease, early detection and treatment is key. After all, you would want to treat it while it is still reversible.
Make an appointment today!
Call us at 6336 6222 or get in touch via our e-appointment form to book your appointment today!